KAUSAT-5
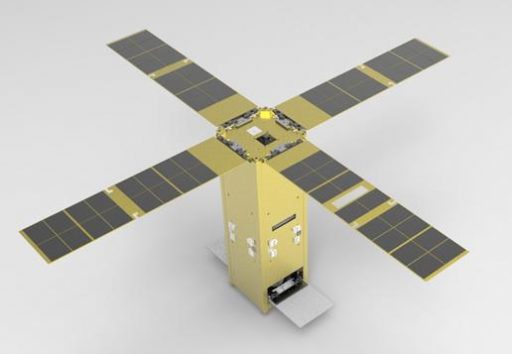
KAUSAT-5 is a triple-unit CubeSat developed and operated by Korea Aviation University with the primary objectives of Earth observation in the infrared band and the measurement of radiation in the Low Earth Orbit Environment. The satellite also serves as a technology demonstrator for satellite components developed and built in-house at the Space System Research Lab
The four-Kilogram satellite has four deployable solar panels for power generation, a deployable sunshield for the IR imager and it carries a Geiger-Müller Counter for the radiation experiment. Other CubeSat elements tested by the mission include an Electric Power System with Maximum Power Point Tracking Capability and a Variable Speed Control Moment Gyroscope for a future development of an agile pointing system for CubeSats. The satellite downlinks at 437.465MHz (telemetry) and 2.413 GHz (IR images & payload data).
Fox 1D
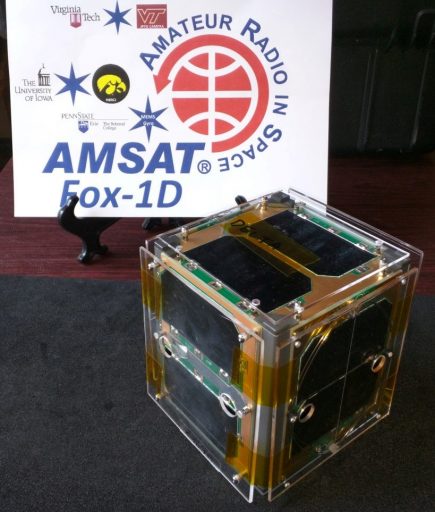

Fox 1D is a 1U CubeSat for amateur radio and technology research developed by AMSAT and hosting a number of university payloads from the University of Iowa Department of Physics and Astronomy, Virginia Tech, and Pennsylvania State-Erie. Is is the third Fox CubeSat to take flight after Fox 1A in 2015 and Fox 1B in 2017 with Fox 1C awaiting launch later in 2018.
The three payloads on the Fox 1D satellite are HERCI from the University of Iowa, a JPEG Camera from Virginia Tech, a MEMS Gyro Experiment from Pennsylvania State-Erie and a L-band uplink system from AMSAT.
HERCI is the High Energy Radiation CubeSat Instrument and designed to map radiation in Low Earth Orbit to collect data for a potential future CubeSat mission hosting detectors for low-energy X-rays. The VT Camera on Fox 1D captures images at 640 x 480 and 320 x 240 resolution.
AMSAT’s payload on the satellite is identical to that on the Fox 1A & B satellites and comprises an FM analog transponder for digital data rates of up to 9600 bps, serving in a U/v repeater function for amateur radio users. The satellite hosts a two-meter and 70-centimeter whip antenna.
Tyvak 61C

Tyvak 61C is a technology demonstration and astronomy mission by California-based Tyvak Nano Satellite Systems with the primary objective of cataloging the variability of luminous stars.
The 3U CubeSat is likely based on the company’s Endeavor satellite platform range – 10 x 10 x 30 centimeters in size when launching, deploying four solar panels, each 10 x 30 cm, that release from the satellite side panels. Endeavor satellite uses an aluminum skeleton and side panels, holding in place the various printed circuit boards that facilitate all the craft’s subsystems and payloads. Li-Ion batteries are used for power storage and attitude determination is primarily accomplished by a pair of star trackers; actuation is provided by a nano-Reaction Wheel Array with three wheels, three integrated torque coils and an optional cold gas propulsion system.
DemoSat-2
DemoSat-2 a U.S. triple-unit CubeSat mission dedicated to testing a UHF radio. Its operator is unknown.
SpaceBEE (4 Satellites)

PSLV C40 is carrying into orbit four SpaceBEE CubeSats for a demonstration of two-way satellite communications and data relay using an ultra-small satellite platform that could enable a cost-effective deployment of a very large number of communications terminals.
The satellites, as shown in ISRO’s mission brochure, are 0.25U CubeSats, only 10 x 10 x 2.5 centimeters in size, and each has a pair of deployable antennas suggesting operation in the VHF/UHF frequency bands.
