LISA Pathfinder Mission Profile

The LISA Pathfinder spacecraft launches atop a Vega rocket from the ZLV Launch Site at the Guiana Space Center in French Guiana. Vega is a four-stage rocket consisting of three powerful solid rocket motors and an Attitude and Vernier Upper Module that uses liquid propellants and can conduct multiple engine burns to allow Vega to access a variety of orbits and perform a precise orbital insertion.
The LISA Pathfinder aims for an elliptical orbit of 207 by 1,540 Kilometers at a low inclination of 5.96 degrees. In this Low Earth Orbit, the spacecraft will complete its Launch and Early Operations Phase that comprises the initial acquisition, establishment of a stable attitude and a series of checkouts and systems reconfigurations. Within three days of launch, the spacecraft will be declared healthy and ready to put to use its Propulsion Module that serves the purpose of boosting the LISA Pathfinder from a Low Earth Orbit to an L1 Transfer Orbit and into orbit around the L1 Sun-Earth Lagrange Point, 1.5 million Kilometers from Earth along the Earth-Sun Vector.
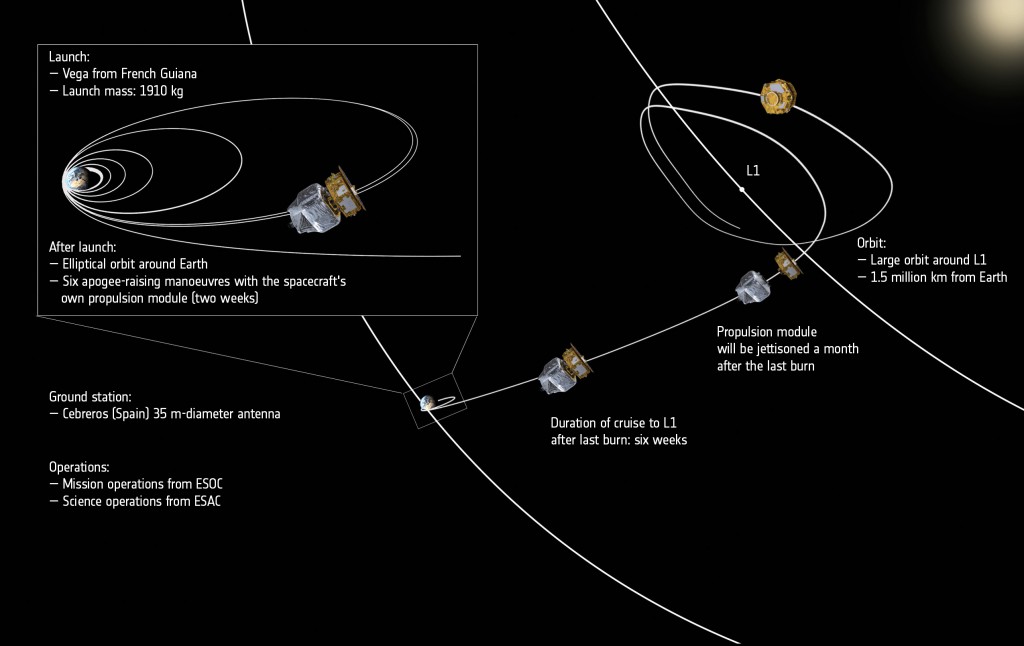
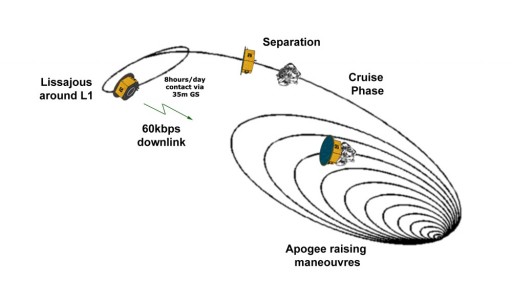
Given the limited performance of the 400-Newton liquid-apogee motor of the Propulsion Module, six firings will be needed to gradually increase the apogee altitude of the Earth-centered orbit over the course of two weeks. The final burn of the Liquid Apogee Engine will deliver the LISA Pathfinder spacecraft to an L1 transfer trajectory in which it will coast for six weeks. Optional Trajectory Correction Maneuvers can be performed to fine-tune the craft’s path towards its targeted orbital insertion point.
The L1 location was chosen for the LISA Pathfinder mission because its environment is suitable for this type of mission and its highly delicate measurements. The L1 orbit provides the spacecraft with a quiet place with respect to its gravitational and magnetic environment as well as a thermally stable location illuminated by the sun at all times. It is located far from any massive bodies that could induce tidal forces on the spacecraft and it allows for constant communications at a low communications delay.
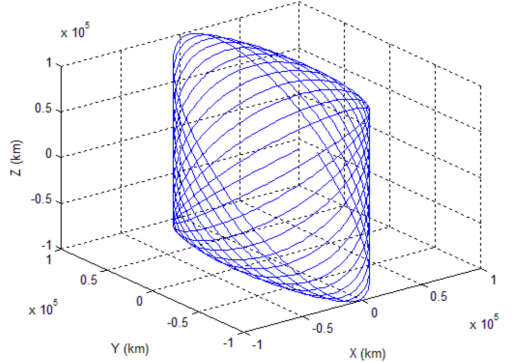
The L1 Lagrange Point offers a semi-stable gravitational environment that allows spacecraft to reside in orbits around the libration point over a period of years at the expense of few propellants for orbit maintenance.
A Lissajous Orbit describes a Lissajous Curve around the Libration Point with components in the plane of the two primary bodies of the Lagrange System and a component perpendicular to it. LISA Pathfinder aims for an L1 orbit of 500,000 by 800,000 Kilometers with a period of 180 days.
In theory, Lissajous orbits are highly stable, but in practice, an orbit around a Libration Point is dynamically unstable – requiring some effort to model as small departures from equilibrium grow exponentially as time progresses. These departures require regular orbit maintenance maneuvers to preserve a stable orbit within mission parameters. The progression of a Lissajous Orbit is largely dependent on its initial parameters – namely phase angle and distance to the L1 point. LISA Pathfinder will use its cold gas thrusters to conduct periodic Stationkeeping maneuvers, expected to require 1.8 meters per second of delta-v per year.
The primary mission of the LISA Pathfinder at L1 will last six months split between 90 days for operations of the LISA Technology Package and Cold Gas Microthrusters and 90 days for the Disturbance Reduction System which also uses the LISA Technology Package as inertial navigation sensor.
Mission Ground Support
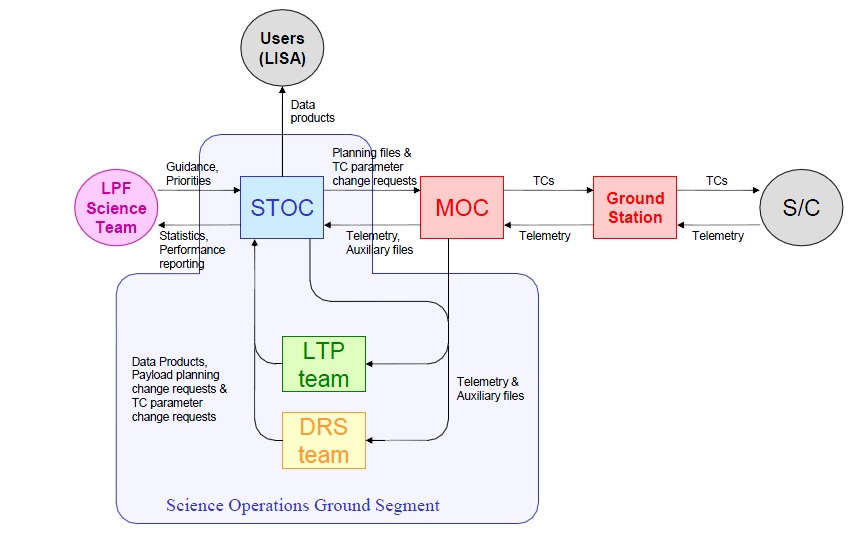
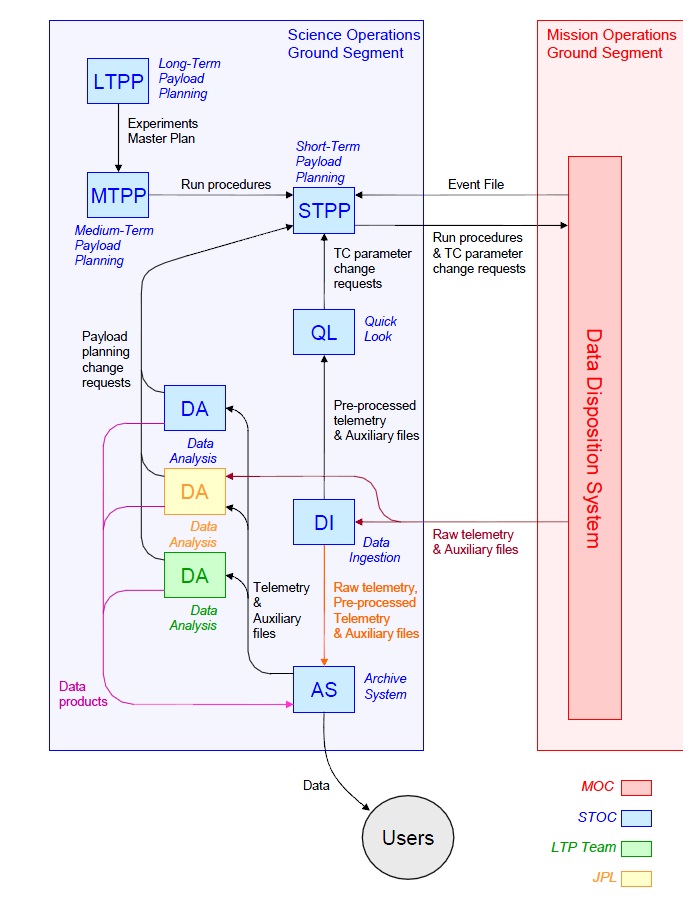
The LISA Pathfinder Ground Segment is comprised to two operational support centers – the Mission Support Center and the Science and Technology Operations Center. The Mission Operations Center is located at the European Space Operations Center in Germany and is responsible for day-to-day mission operations during the Low Earth Orbit Phase of the mission, the transfer to L1 and the routine mission operations phase. Support operations include spacecraft health monitoring, data acquisition from the spacecraft, regular maintenance operations and response to any off nominal situations.
The Science and Technology Operations Center is in charge of operating the spacecraft payloads, scheduling operations and dealing with the mission data. Data from the spacecraft is analyzed for quick-look data products, is processed into calibrated data products, is distributed to participating institutions and is archived for future reference. STOC is also located at ESOC to ensure a close contact between the science operations team and the mission operations support team.

There are three different planning schemes involved in the LISA Pathfinder Mission – long-term, medium-term and short-term planning. The Long-Term Payload Planning looks at high-level planning decisions comprising the next 90 days of mission operations, in particular the definition of experiments to be performed over this time period, the creation of operational plans and the submission of Experiment Master Plans. Medium-Term Payload planning is concerned with the validation of operational requests and the creation of a time-tagged list of telecommands to be sent to the spacecraft for the execution of the requested science sequence. Short-term planning operations concern the submission of Payload Operational Requests to the Mission Operations Center.
LISA Pathfinder can communicate with the ground eight hours every day. Data collected during each day’s ground pass is evaluated by the Mission Operations Center concerning spacecraft health while payload data is relayed to the Science and Technology Operations Center for conduct a quick-look analysis to monitor the operation of the LISA Test Package. Data analysis and Science Archiving will also be completed at STOC.
