NuSTAR X-Ray Observatory begins two-year Extended Mission
Originally published July 31, 2014
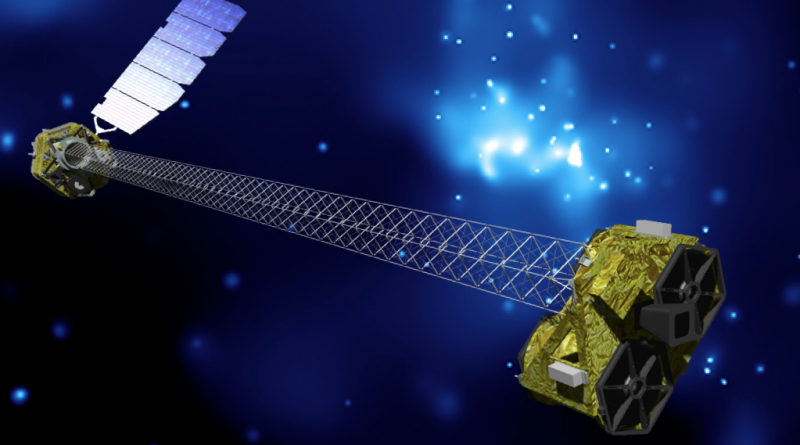
NASA’s NuSTAR spacecraft, the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, has successfully completed its two-year primary science mission following its launch on June 13, 2012 and is now transitioning to an extended mission to continue its studies of X-Ray sources in the sky, also starting its Guest Observer program to give scientists around the world observation time on the spacecraft.
“It’s hard to believe it’s been two years since NuSTAR launched,” said Fiona Harrison, NuSTAR principal investigator. “We achieved all the mission science objectives and made some amazing discoveries I never would have predicted two years ago.”
Over the course of its primary mission, NuSTAR observed black holes, supernova remnants, galaxy clusters and other objects. Its vision tuned to the most energetic portion of the X-Ray spectrum, NuSTAR provided extremely valuable data to complement and expand measurements made by other ground- and space-based observatories to help unlock mysteries revolving around black holes and supernovae.
The mission shed light on the previously unknown properties of ultraluminous X-ray sources, delivered unprecedented data explaining how stars explode and unlocked the processes driving the rotation of massive black holes.
With its primary mission complete, NuSTAR will move on to a new chapter while scientists are still pouring over data provided during the first two years of observations. Over the next two years, NuSTAR will continue looking at black holes, supernovae and other targets including targets of opportunity and integrated observations with other observatories.
NuSTAR’s Guest Observer Program will begin next spring to give scientists not part of the mission the opportunity to pick targets to be observed by the spacecraft. About 50% of the observation time will be dedicated to guest observers from around the world to increase the scientific return from the mission.
NuSTAR is currently funded through fiscal year 2016 to complete its extended mission.