PACE
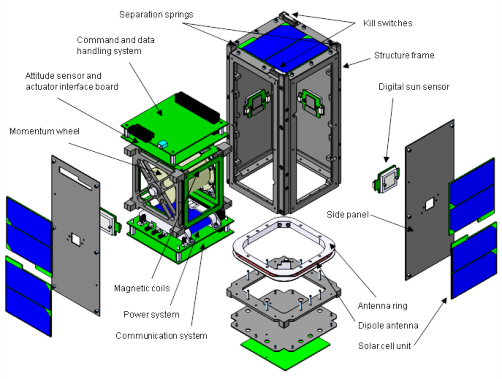
PACE – Platform for Attitude Control Experiments – is a project of National Cheng Kung University, Taiwan that was initiated in 2003. The 2U CubeSat is 112 by 112 by 243 millimeters in size and weighs less than 2 Kilograms hosting an experimental attitude determination and control system for testing in orbit.
The spacecraft consists of an aluminum framework and panels. 20 body-mounted triple-junction GaAs solar cells are used to generate two watts of power that is stored in Li-Ion batteries with an capacity of 3.6Ah. PACE uses a 3.3 and 5V power bus. Communications are accomplished via UHF using the 437MHz frequency. The satellite is controlled by an 8051 microprocessor that uses 16MB of flash memory for data storage.
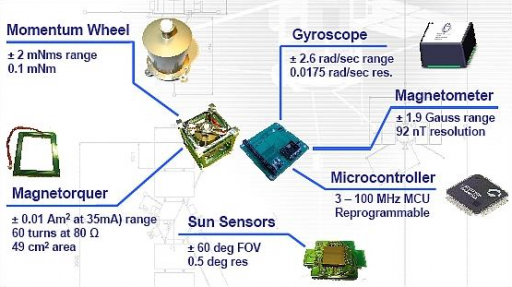
The Attitude Determination and Control System of the PACE satellite consists of four digital sun sensors, a three-axis magnetometer and three gyroscopes for precise attitude determination and a momentum wheel assembly and magnetic coils for three-axis attitude actuation. The wheels spin at 2000rpm with a momentum capacity of 0.002Nms, the Digital Sun Sensors have a field of view of +/-60 degrees and provide an accuracy of 1 degree.
Throughout its mission, the satellite will downlink attitude information to evaluate the performance of the attitude control system. Using many newly developed components, PACE will also demonstrate these various systems in the space environment for potential use on future missions. Over the course of the mission, PACE will run different attitude control laws that are uplinked during the mission and executed sequentially.
After attitude testing is complete, the satellite enters an automatic mode to study the behavior of its systems in the space environment over an extended period of time.
