Ekspress AM-7

Ekspress AM-7 is a Geostationary Communications Satellite providing Internet, TV and radio broadcasting under operation by the Russian Satellite Communications Company. The satellite was built by Airbus Defence and Space to join the existing fleet of Ekspress satellites to ensure a continued expansion in services. The spacecraft will provide coverage to regions of Africa, Central and Eastern Europe.
The Ekspress satellite program has been initiated in 1994 to provide communications to the civilian and commercial sectors, replacing the older Gorizont Communications Satellites. The overall goal of the Ekspress program was to close the technology gap between Russian and Western comm satellite manufacturers.
Between 1994 and 2001, two first generation Ekspress satellites and four improved Ekspress A satellites were launched (one was destroyed in a launch failure). The Ekspress AM series of satellites was inaugurated in 2003 and represents powerful communication satellites with long on-orbit service lives and flexible communication payloads.
Fourteen Ekspress AM satellites were launched to date – Ekspress AM-4 did not reach its correct orbit in 2011 and was disposed via a targeted re-entry and its replacement satellite was lost in a Proton-M launch failure in May 2014. In addition to Ekspress AM satellites, Ekspress MD satellites are being launched to maintain an alternate supplier of communications satellites as the MD spacecraft are built by Khrunichev.
Two Ekspress MD satellites were launched in 2009 and 2012, but the last launch left the satellite in a useless orbit after an upper stage failure – three more MD satellites are on contract for launch in the next decade. Ekspress AM-5 was launched in late 2013 and represented the most powerful commercial communications satellite launched in the Ekspress series. In 2014, a duo of Ekspress AT satellites was delivered to orbit to provide communication services across the entire Russian territory. The Ekspress AM-6 satellite, also built by Reshetnev, was launched in 2014 providing C- and Ku-Band coverage to Russia, Europe and Africa.
Over the coming years, new Ekspress versions will be inaugurated including the AMU and RV series while launches of the AM series will continue.
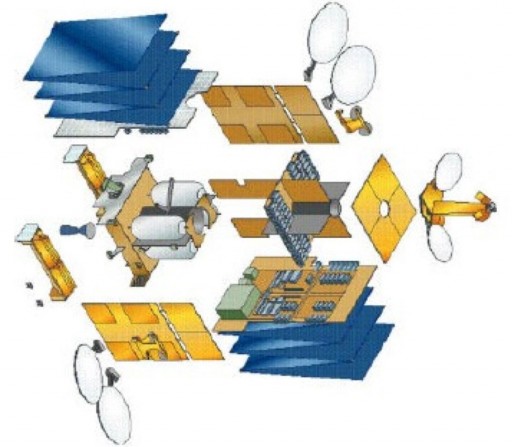
Ekspress AM-7 uses the flight-proven Eurostar-3000 Platform manufactured by Airbus Defence and Space. The platform is capable of hosting communications payloads with a total power exceeding 16,000 Watts. The spacecraft platform can support a high degree of customization to be able to support a variety of payloads including commercial communications and military payload packages. Eurostar-3000 made its first launch in 2004.
The Ekspress AM-7 satellite has a launch mass of 5,720 Kilograms with a payload mass of 1,438.5 Kilograms. The spacecraft stands 7.5 meters tall and, in orbit, its deployed solar arrays have a span of over 30 meters.
The satellite platform consists of a central cylinder which facilitates the propellant tanks for the bi-propellant propulsion system. The cylinder consists of several segments connected via ring-joints. Internal composite panels are mounted to the cylinder to facilitate the external panels and provide mounting platforms for the various satellite components.
Two deployable solar arrays are used for power generation featuring triple-junction Gallium-Arsenide solar cells. Power is stored in onboard batteries while a Power Conditioning and Distribution Unit regulates the satellite’s power bus and controls the state of charge of the batteries. At the start of its mission, Ekspress AM-7 will generate a total power of 18,000 Watts dropping to 16,000 Watts towards the end of its mission with a nominal payload power around 13,665 Watts.
A dedicated bi-propellant propulsion system will be used for apogee maneuvers and stationkeeping maneuvers in Geostationary Orbit. Eurostar-3000 is three-axis stabilized featuring a state of the art navigation system. The satellite provides precise Earth-pointing capabilities and stationkeeping accuracy is +/-0.05 degrees. E-3000 provides the option of adding an electric propulsion system.
Ekspress AM-7 hosts a multi-band payload consisting of 24 C-Band, 36 Ku-Band and two L-Band transponders.
One fixed C-Band coverage zone is provided by the spacecraft, stretching from Western Europe (Great Britain and France) all the way to central Russia and Kazakhstan, stretching down to Saudi Arabia. A steerable C-Band coverage zone will be provided to cover emerging markets in Africa. Three fixed Ku-Beams are generated by the satellite: one covering a large portion of Europe reaching from Spain to the Ukraine and as far south as Egypt, one covering Eastern Europe up to Central Russia, and a third covering the Indian subcontinent and surrounding territories. Coverage to Africa will be provided by a steerable Ku-Band beam.
Ekspress AM-7 will be operated from Geostationary Orbit at a position of 40 degrees east for an operational lifetime of 15 years.
