NORSAT 2
NORSAT-2 is a ship-tracking and Low Earth Orbit communications satellite operated by the Norwegian Space Center (Norsk Romsenter) to deliver advanced ship-tracking data over the territorial waters of Norway and provide a new VHF data exchange system serving the high-altitude regions.
The satellite is based on the Generic Satellite Bus provided by the University of Toronto, Institute for Aerospace Studies; largely similar to NORSAT-1 that launches on the same Soyuz rocket as NORSAT-2.
The NORSAT-2 satellite measures 20 x 30 x 44 centimeters in size and weighs 16.7 Kilograms of which 1.3kg can be attributed to the AIS payload and 1.5kg for the VDES payload plus 0.3kg for an innovative antenna system. Both payloads were developed and built at Kongsberg Seatex, Norway with the AIS payload in use by the Norwegian Coastal Authority and the VHF communications payload owned by Space Norway.
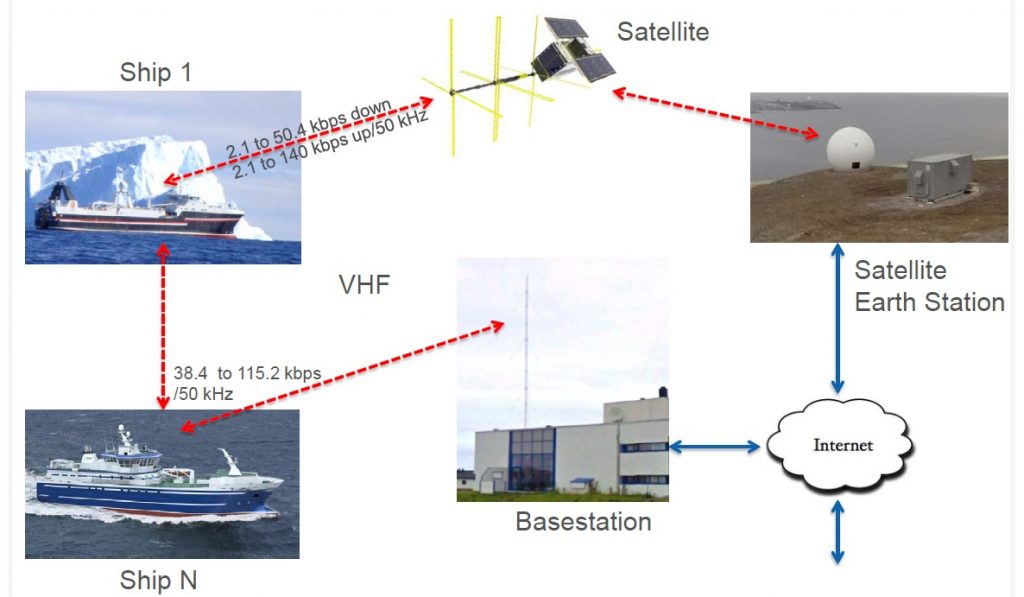
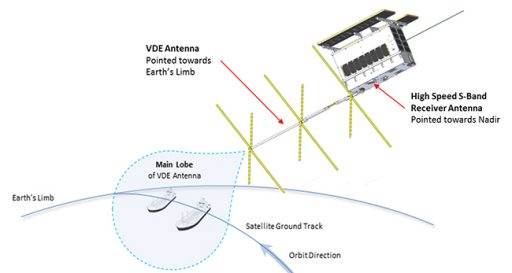
The VHF Data Exchange (VDE) payload employs a new type of deployable crossed Yagi antenna that allows small satellite missions to use a directional VHF antenna. NORSAT’s Yagi antenna measures 80 by 97.5 centimeters in size when in its deployed state and the payload uses the 157.1875-157.3375 MHz band for data uplink and 161.7875-161.9375 MHz for transmission. The payload primarily relies on a Software Defined Radio that allows for in-flight reconfigurations to optimize the satellite for different tasks. VDE will operate at uplink data rates of up to 50.4 kbps and downlink up to 140 kbps, providing higher data rates than the baseline AIS system.
VDE integrates AIS with Application Specific Messages (ASM), which are new channels with more capacity and better reliability of message delivery. Taking advantage of a polar orbit, NORSAT-2 will provide eleven minutes of communications coverage over the Norwegian and far north territories out of every 97-minute orbit.
NORSAT-2 features a pair of deployable solar arrays and body-mounted panels with a peak power generation of 56 Watts. The Generic NanoSatellite Bus provides all structural support, power supply, thermal control, attitude determination/actuation, data handling and communications. An S-Band feeder link at 1Mbps is used for up and downlink of data stored on the satellite including AIS messages.
