VELOX II Satellite

The VELOX II Nano-Satellite is an experimental satellite developed and operated by the Nanyang Technological University. Weighing in at 13 Kilograms, the satellite follows the 6U CubeSat form factor, measuring 12 by 24.6 by 34 centimeters in size when in its stowed configuration. The primary purpose of the satellite is a demonstration of an inter-satellite communications system and testing of fault tolerant GPS receivers and other electronics in the operational space environment.
The satellite consists of an aluminum chassis and stainless steel load bearing structures, spring loaded deployment systems and an extendable optical mechanism. Two 6U solar panels are stowed against the satellite side panels during launch and deploy in orbit to deliver power to the satellite along with two fixed 3U solar panels. The six arrays with a 2 series, 5 parallel cell layout can deliver a peak power of 40.8 Watts while the smaller panels generate up to 6 Watts of electrical power. Power is stored in a 11.6 Amp-hour battery delivering a nominal bus voltage of 7.2 V.

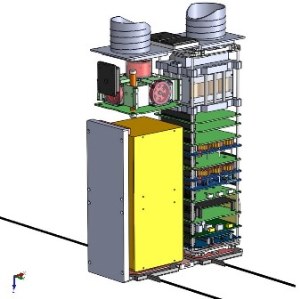
The VELOX II satellite uses an active attitude control system comprised of three reaction wheels and three magnetic torquers for precise attitude actuation and fine and coarse sun sensors for attitude determination, assisted by two Inertial Measurement Units and a GPS unit for orbit determination. Data handling and satellite control is provided by a central mainboard with a 100 MHz 8051 MCU with a 2 GB SD card for data storage. Internal communications are handled by UART and I2C data interfaces. Communications with the ground use a UHF system for downlink at 9600 bits per second while uplink is accomplished using a 1200bps VHF terminal.
The primary objective of the VELOX II satellite is the demonstration of an inter-satellite communications system for the transmission of data to satellites in Geostationary Orbit so that smaller low-orbiting spacecraft can deliver data in real time. A secondary objective of the mission is to demonstrate precision navigation and fault tolerant electronics.
