GOES-R Ground Segment
The GOES-R-class satellites come with an integrated ground system – a first in the history of GOES. Ground Segment capabilities include data processing, satellite control, mission planning and performance monitoring. In charge of ground system development is Harris Corp. tasked with establishing a system that can reliably process and distribute GOES data products to a worldwide community of users.
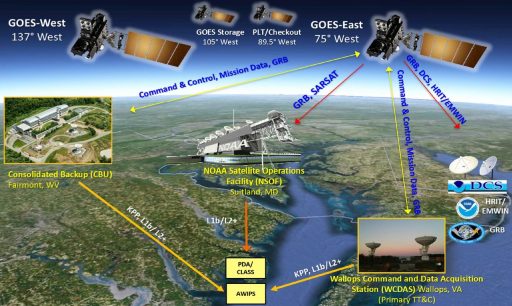
GOES Mission Operations are directed from the NOAA Satellite Operations Facility (NSOF) in Suitland, Maryland and the primary Command and Data Acquisition Station is located in Wallops, Virginia with a backup station in Fairmont, West Virginia that can also support Product Generation and Product Distribution normally completed by the Ops Facility. Overall, the ground segment comprises 2,100 servers, 149 Network Racks, 317 workstations, and data storage totaling 3 Petabytes. Product processing is completed by 454 blade servers with 3,632 processor cores capable of 40 trillion floating point operations per second.
Both the primary and backup have been outfitted with new 16.4-meter antennas to be able to support the GOES-R infrastructure as well as the heritage GOES service. They are designed to operate through a Category 2 Hurricane with no degradation.
The GOES Ground Segment fulfills the following functions:
Mission Management: The MM Element of the Ground Segment represents the primary interface between the ground segment and the satellites – tasked with space-to-ground communications, command generation, telemetry reception and processing, mission planning and operations, and data product monitoring.
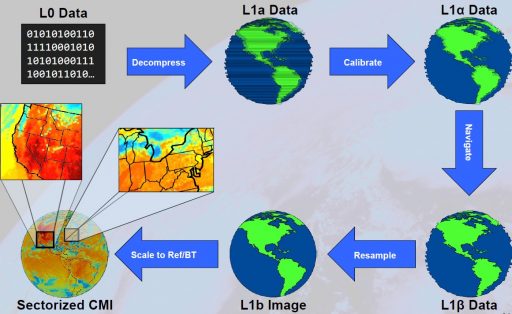
Product Generation: Raw signals received by the ground stations are processed back into CCDSD-formatted packets which are then converted to Level 0 Products – reprocessed, unreconstructed instrument data at full resolution, free of communications artifacts. Radiometric and geometric correction via calibration and navigation data yields Level 1b radiance data which can then be processed into higher data products. L2+ data from the GLM instrument plus L1b data from all other instruments is part of the GOES Re-Broadcast Link that sends the data to the GOES satellites in X-Band where it is then converted to an L-Band signal for immediate downlink to users.
In total, there are 65 data products generated by the GOES instruments, 56 of which come from the Advanced Baseline Imager alone. ABI products cover atmospheric properties, ocean and land data as well as clouds, radiation and precipitation. GLM delivers near real-time lightning products including lightning maps and severe weather warnings. The space weather instruments generate 8 products for use by the Space Weather Prediction Center.
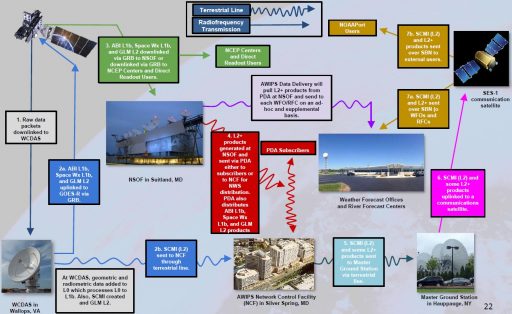
Product Distribution: The GOES-R Access Subsystem is the primary source for GOES End Products. It contains a seven-day data repository and data interface for subscription-based and ad hoc data requests. The National Weather Service receives data through the Advanced Weather Interactive Processing System that offers lower latencies. Each satellite generates around 2.5TB of data per day (L0, L1b and L2+) products which are archived at the CLASS (Comprehensive Large Array-data Stewardship System) repository to be available for climatological and other studies.
GOES Unique Payload Services
The GOES-R Unique Payload Services suite hosts a number of transponders to send and receive different types of data in support of communications relay that is not part of the core GOES mission data.
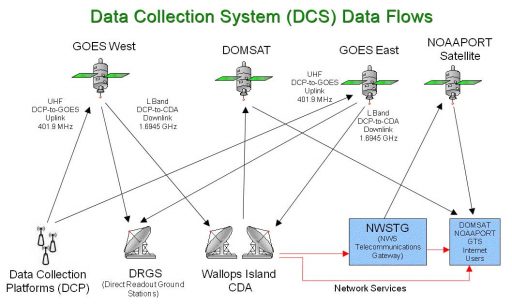
GOES-R supports the data collection system featuring a UHF antenna to receive messages from DCS Platforms deployed in remote locations on Earth. DCPs can be deployed virtually at any location on the globe to provide in-situ measurements of meteorological data that is then uplinked to satellites and transmitted to ground stations for collection, processing and distribution. The DCPs operate in the UHF band at 401/402 MHz. These platforms include remote weather stations, buoys at sea to measure sea state and alert in the event of tsunamis as well as other measurement stations that are deployed in remote locations.
GOES-R Rebroadcast Services represent the primary space-based relay of GOES data products comprised of Level 1b products for all instruments with the exception of GLM that delivers L2+ products. This calibrated, full-resolution data includes all ABI channels in a lossless compression formation and data from all other instruments, offered free of charge to all users that have the required technology for receiving the data. GRB data is delivered to the satellite via X-Band and converted to a 31MBit/s L-Band signal to be received by ground stations operated by a wide user base.
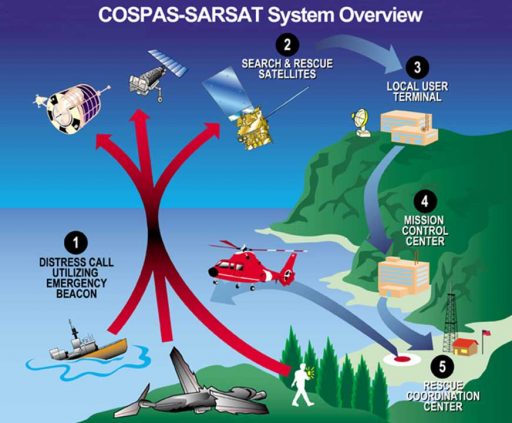
The SARSAT (Search and Rescue Satellite Aided Tracking) System enables the relay of distress signals from mariners, aviators, and other recreational users in distress at any position within the satellite’s footprint. The task of the spaceborne terminal is to relay distress calls to the SARSAT Mission Control Center which then sends them to the closest Rescue Coordination Center to begin the search and rescue effort in the area.
