AMOS 6 Satellite

AMOS 6 is a Commercial Communications Satellite built by Israel Aerospace Industries for operation by Israeli telecommunications provider Spacecom as part of the AMOS series of “Affordable Modular Optimized Satellites.” Spacecom announced in August that the company is being sold for $285 million to Beijing Xinwei Technology Group in a deal that includes the AMOS-6 spacecraft, to be launched in early September by a Falcon 9 rocket.
AMOS 6 is the second satellite utilizing the AMOS-4000 satellite platform offered by IAI as the largest of the company’s satellite buses in the 3 to 5.5-metric ton weight class with an onboard power supply between 3 and 12 Kilowatts. Larger than previous AMOS buses, the platform still uses a modular design comprised of the bus, repeater and antenna modules.
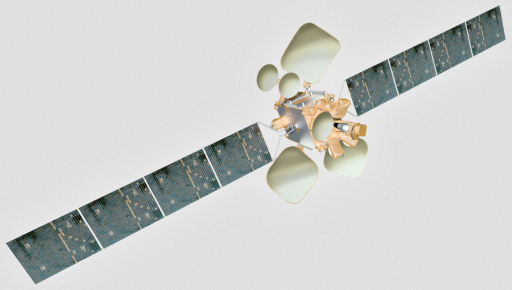
Spacecom announced in 2012 that it signed a $195 million deal with IAI for the construction of the AMOS 6 satellite to become the newest addition to the AMOS fleet, replacing the aging AMOS-2 satellite that launched in 2002 and is to be retired in 2017. SpaceX was announced as the launch services provider in 2013 with $85 million set aside for the launch vehicle, launch insurance and the first year of the satellite’s operation.
The satellite hosts 39 Ku Segments and 24 Ka-Band beams plus two S-Band transponders to create three Ku-Band beams covering the Middle East, Central Eastern Europe and a Pan-European band, and 36 Ka-Band spot beams focused on Sub-Saharan Africa and Europe.
AMOS 6, stationed at 4° West in Geostationary Orbit, strengthens Spacecom’s existing service supporting a number of applications that include Direct-To-Home Television, video distribution, VSAT communications, and broadband internet connectivity.

A portion of the satellite’s Ka-Band payload has been leased to Social Media company Facebook and telecom provider Eutelsat in a $95 million deal covering five years. The capacity with an approximate throughput of 18 Gigabits per second will be used for Facebook’s Internet.org that aims to bring affordable Internet services to developing areas.
The AMOS 6 satellite has a liftoff mass of 5,400 Kilograms and hosts two four-panel solar arrays to deliver a power of 10 Kilowatts. The satellite combines chemical propulsion for orbit raising with electrical propulsion systems for stationkeeping in Geostationary Orbit. The vehicle is equipped with an S400 Propulsion System for apogee burns and larger orbit maintenance maneuvers. The S400 series built by Airbus Defence and Space are bi-propellant engines using Monomethylhydrazine and Mixed Oxides of Nitrogen as propellants. Depending on the version used, S400 provides 420 to 425 Newtons of Thrust with a specific impulse of 318-321 seconds.
Thales Alenia provided the electric propulsion system and Canadian company MDA was contracted to build the communications payload. The satellite has been built for at least 15 years of operation co-located at Spacecom’s prime orbital position, enabling satellite redundancy, backup capabilities and high service reliability.
