Ekspress AM-6

Ekspress AM-6 is a Geostationary Communications Satellite built by ISS Reshetnev to be operated by the Russian Satellite Communications Company as part of the existing Ekspress satellite fleet that provide a variety of communication services to Russian and surrounding territories. The payload of the AM-6 satellite was built by MacDonald, Dettwiler and Associates Ltd. (MDA), Canada.
The Ekspress satellite program is used to provide communications to the civilian and commercial sectors having been initiated in 1994 to replace the aging Gorizont communications satellites.
The Ekspress program had the overall goal to close the technology gap between Russia and Western comm satellite manufacturers. Between 1994 and 2001, two first generation Ekspress satellites and four improved Ekspress A satellites were launched (one was destroyed in a launch failure).

The Ekspress AM series of satellites was inaugurated in 2003 and represents powerful communication satellites with long on-orbit service lives and flexible communication payloads. Thirteen Ekspress AM satellites were launched to date – Ekspress AM-4 did not reach its correct orbit in 2011 and was disposed via a targeted re-entry and its replacement satellite was lost in a Proton-M launch failure in May 2014. In addition to Ekspress AM satellites, Ekspress MD satellites are being launched to maintain an alternate supplier of communications satellites as the MD spacecraft are built by Khrunichev.
Two Ekspress MD satellites were launched in 2009 and 2012, but the last launch left the satellite in a useless orbit after an upper stage failure – three more MD satellites are on contract for launch in the next decade. Ekspress AM-5 was launched in late 2013 and represented the most powerful commercial communications satellite launched in the Ekspress series. In 2014, a duo of Ekspress AT satellites was delivered to orbit to provide communication services across the entire Russian territory.

Over the coming years, new Ekspress version will be inaugurated including the AMU and RV series while launches of the AM series will continue.
Ekspress-2000 is a satellite platform developed by ISS Reshetnev to host large communication payloads as opposed to the smaller Ekspress-1000 satellite bus that had become operational earlier. The satellite platform is capable of hosting payloads of more than one metric ton with a payload power topping out at 15kW.
Ekspress AM-6 weighs 3,350 Kilograms and features two power-generating solar arrays, each consisting of five panels, to deliver 14,200 Watts of power to the satellite for distribution to the various satellite systems and the communications payload. The satellite is three-axis stabilized with precise pointing capability and stationkeeping accuracy of 0.05 degrees. An electric propulsion system is used for orbital maneuvers and orbit maintenance. Ekspress AM6 is planned to operate for at least 15 years from an orbital position of 53° East in Geostationary Orbit.
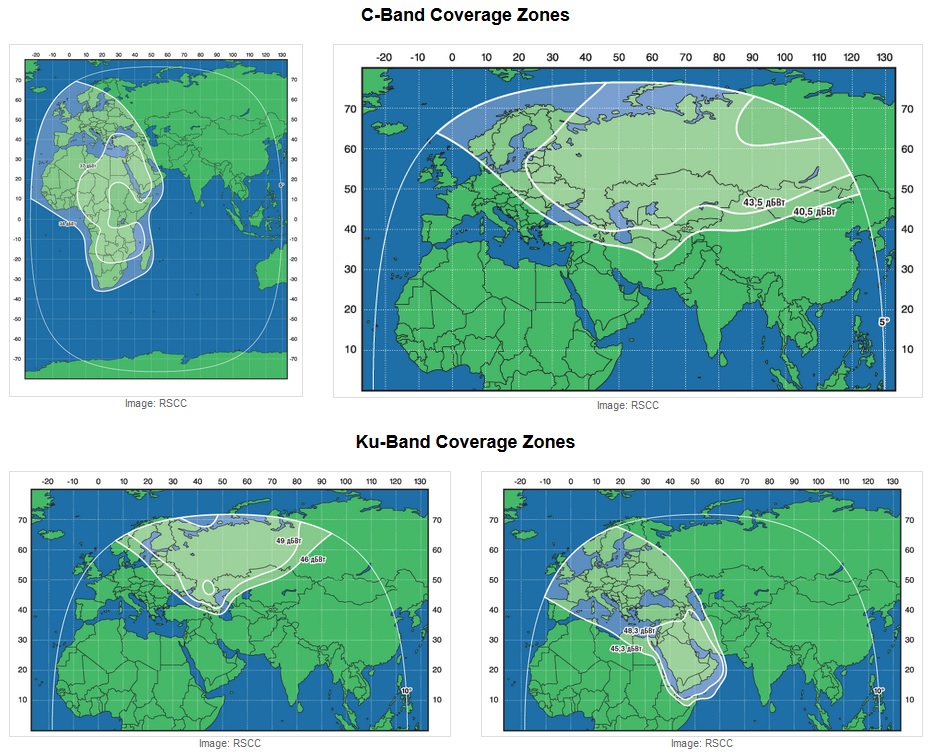
The Ekspress AM-6 satellite is equipped with a total of 72 transponders operating in four different frequency bands using 11 antenna reflectors installed on the spacecraft. 14 C-Band transponders are installed on the spacecraft creating two fixed zones and a global beam.
The first fixed zone covers a large portion of Russia with the exception of the Eastern part of the country, the zone also covers Kazakhstan and eastern Europe. The Second C-Band beam covers the entire continent of Africa, Saudi Arabia and western and central Europe. The global C-Band beam provides coverage of the entire continent of Europe and Africa also covering portions of Asia and Australia.
Two fixed and two steerable Ku-Band beams are served by 44 active Ku-Band transponders. The fixed Ku-Zones include a Russian Beam that covers the western half of the country and portions of eastern Europe while the second Ku-Zone stretches from the Middle East all the way across Central Europe into the northern countries. The mobile Ku-Beams can be used to provide communications coverage to regions of high demand.
12 Ka-Band transponders are used to provide coverage across ten Spot Beams spaced over Russia and eastern Europe. Two L-Band transponders are also installed on the satellite.