Argus
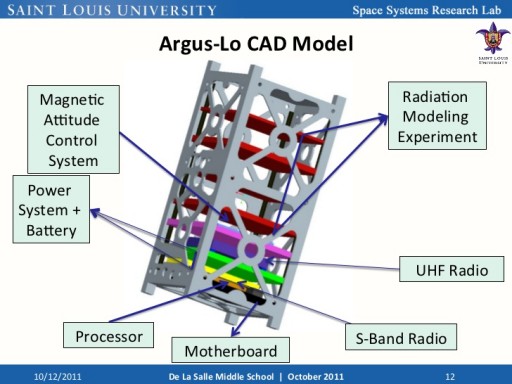
Argus, also known as SLU-02, is a 2U CubeSat that is the result of a collaborative project between the Space Systems Research Laboratory at St. Louis University and the Institute for Defense and Space Electronics (ISDE) at Vanderbilt University. The goal of the mission is to explore and model the effects of space radiation on modern electronics systems. This will be accomplished by comparing a predictive models developed at Vanderbilt with the measured rates of in-orbit radiation events.
The 10 by 10 by 20-centimeter satellite has a mass of 3.0 Kilograms based on the SCARAB satellite bus – the SLU Core Aerospace Research Application Bus designed as a one-size-fits-all, multi-mission CubeSat bus for fast implementation of missions hosting various payloads. The satellite uses a structural frame provided by Pumpkin Inc., incorporating a PIC-24 CubeSat Kit Microcontroller, body-mounted solar panels & Li-Ion/polymer batteries and a UHF/VHF transceiver for communications. The satellite uses a passive attitude control system.

The motivation behind Argus is the current state of radiation models with respect to the effect of radiation on electronics which are based on electronics standards from the 1970s and 80s and computational resources from the same period. Modern electronics are completely different in architecture, much smaller, faster and more complex than the systems of three decades ago. Therefore, LSU concludes, the existing models are not applicable to today’s space systems and new data is needed to revise the models.
Researchers at Vanderbilt came up with new prediction models, but these models require verification and calibration in an actual space environment with its characteristic particle inflow and particle energies. The heart of the Argus satellite is the Independence Payload developed at Vanderbilt, coupled with the Vanderbilt University Controller which is in charge of logging all radiation-induced events for later downlink to the ground. The Independence Payload includes three experiments – a single-event upset detection system, a single-event latchup experiment, and a particle environment monitor.
