Superbird 8 / DSN 1
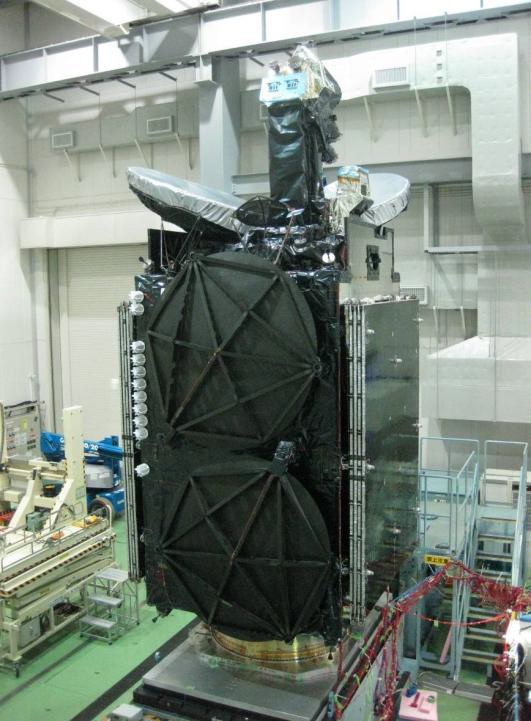

Superbird 8 / DSN 1 is a dual-use communications satellite carrying a commercial Ku/Ka-Band payload operated by SKY Perfect JSAT to serve the Japanese market and an X-Band terminal for use by DSN Corporation as the second of two DSN satellites delivering secure connectivity for government and military use.
Superbird 8 with the DSN 1 hosted payload was originally planned to launch in 2016, but when being transported to its French Guiana launch site that May, the satellite experienced an overpressurization event within its sealed, environmentally-controlled transport container. This caused significant damage to the Mitsubishi-built satellite which had to be shipped back to Japan for repairs and detailed re-testing – setting its project schedule back by nearly two years.
SKY Perfect JSAT is among the largest commercial satellite operators in Asia, forming in 2007 out of the merger of JSAT that finds its roots in 1985 and the pay TV business Sky Perfect TV that was founded in 1994 as a multi-channel pay-TV company. The JSAT satellite fleet started out in 1989 and has since seen a total of 31 satellites launched of which 28 successfully entered operations under various designations including the fully-owned JCSAT and Superbird series and the acquired or co-owned N-STAR and Horizons satellites. The company also provides operational services like management services of the DSN network in which JSAT is involved as the majority owner.
DSN Corporation is a joint venture between satellite operator SKY Perfect JSAT, technology company NEC, telecommunications provider NTT Communications, and civil engineering company Maeda Corporation. The Japanese Ministry of Defence awarded a contract to DSN Corp. in January 2013 covering the provision of an upgraded space segment for Japan’s military X-Band network, ground systems upgrades and the operation of the system through the year 2030.
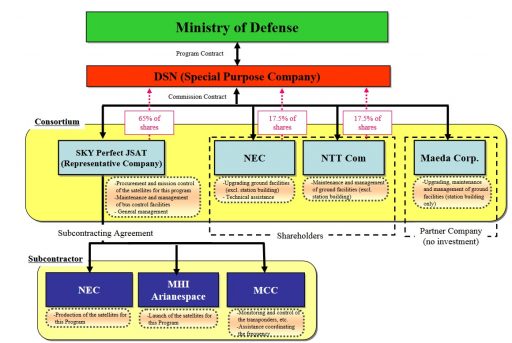
DSN was Japan’s first Private Finance Initiative that uses private funds, management and technical capabilities with the involved companies incurring the capital investment of the project and then drive in annual revenue from the Japanese government through the end of the program around 2031.
Sky Perfect JSAT owns 65% of DSN Corporation and is responsible for the overall coordination of the project, procurement and operation of the space segment, and maintenance of bus control facilities. NEC and NTT each own 17.5% of shares with NEC responsible for the ground segment upgrade and technical assistance and NTT in charge of ground segment maintenance and management. Maeda has no investment in the company and acts as a partner, tasked with building new ground stations for the DSN system.
The DSN Network comprises two space segment components – DSN-1 is a hosted X-Band payload on the Superbird-8 satellite and DSN-2 is a dedicated satellite. Due to the delay encountered by DSN-1, the DSN-2 satellite launched before it, riding into orbit atop a Japanese H-IIA rocket in January 2017.

Superbird-8, to be-renamed Superbird-B3 once in orbit, was ordered by JSAT from Mitsubishi Electric in April 2014 for launch approximately two years later. The lengthy delay incurred by the Superbird 8 satellite required JSAT to put JCSAT-16 – a dedicated backup spacecraft for cases such as this – into operation to fill in for Ku/Ka-Band capacity from Superbird 8 that had already been sold. Launched by a Falcon 9 rocket in 2016, the SS/L-built Ku/Ka-Band satellite was commissioned by JSAT to serve as an in-orbit backup capable of filling in for satellites encountering technical problems or providing gapfiller capabilities.
After the lengthy delay for Superbird 8 became known, JSAT moved JCSAT-16 from 124°E into the planned B3 position at 162°E.
Superbird 8 is intended to replace the Superbird-B2 satellite launched in February 2000 atop an Ariane 5 rocket and outfitted with 23 Ku-, 6 Ka- and one steerable Ku-Band beams to deliver business telecommunications services.
Through the use of modern-day communications technology, Superbird 8 will provide full replacement coverage plus expansion capacity to provide additional services to the growing VSAT customer base across Japan.
MELCO’s DS-2000 satellite platform originated in a satellite design of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency that was modified by Mitsubishi Electric to create a versatile geostationary satellite platform for use in commercial communications satellites, weather satellites, data relay craft and navigation satellites. DS-2000 first flew in 2002 and is highly regarded across the commercial space sector for its excellent reliability and projected mission durations in excess of 20 years.
DS-2000 can support a payload power of up to 15 Kilowatts and has been baselined for a 100-Volt power bus that implements redundancy to ensure all equipment of the satellite receives electrical power. Power storage is typically accomplished with a 175 Amp-hour battery unit and dedicated electronics are used for power distribution and bus protection.
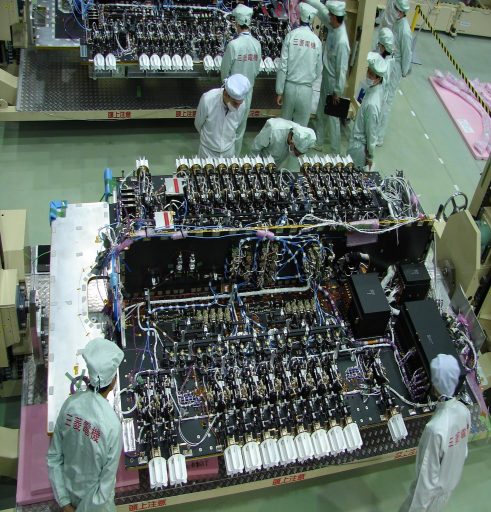
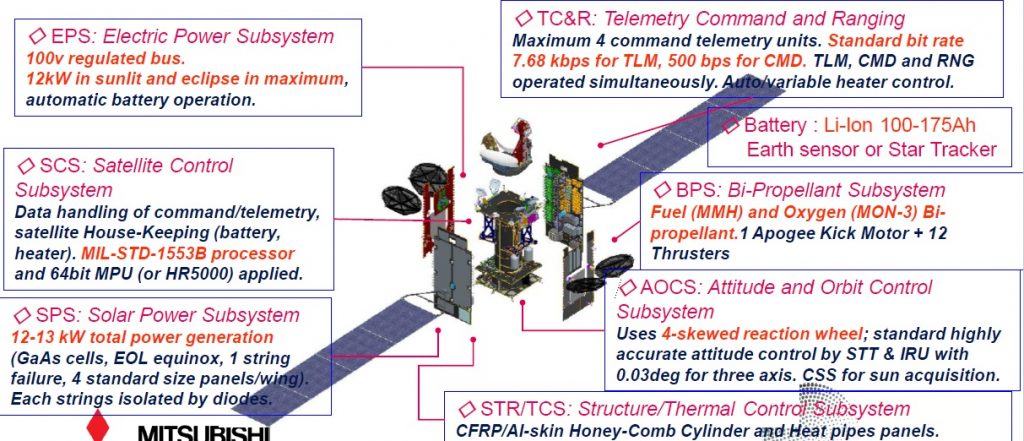

Structurally, the satellite consists of an internal cylinder that builds that load-bearing structure of the spacecraft and facilitates the propellant tanks. From the cylinder extends a network of struts and panels made of Aluminum skin Carbon-Fiber-Reinforced Plastic, used to provide mounting surfaces for the various subsystem components.
Attitude determination primarily relies on a Star Tracker system and Inertial Reference Units as well as Earth and Sun Sensors used during initial acquisition and safe mode. Using a Reaction Wheel Assembly consisting of four wheels, the satellite has a pointing accuracy of 0.03 degrees for precise Earth-oriented operation. Thermal control equipment on the satellite includes external radiators and internal heaters to maintain an operational environment for all satellite components.
DS-2000 features a liquid-fueled propulsion system consisting of an Apogee Engine and a dozen attitude control thrusters. The main engine is located on the aft side of the spacecraft and is used to perform a series of apogee maneuvers to boost the satellite from an elliptical Geostationary Transfer Orbit into a nearly circular Geostationary Orbit. Engine options available for the DS-2000 satellite bus are the 490-Newton R-4D and 450-Newton BT-4 engine, both use Monomethylhydrazine and Nitrogen Tetroxide/MON as propellants.
Details and specifications of the X-Band payload of the DSN satellites are not available to the public given the military nature of the mission. The satellite will be used to connect Japanese military units on land, naval vessels and the air forces of Japan.
